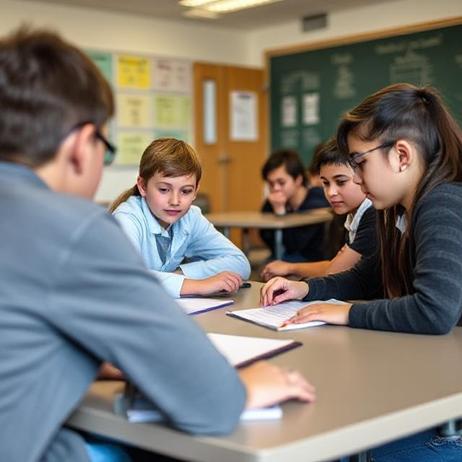
How Boarding Schools Support Students with Learning Differences
As of 2025, the landscape of education for students with learning differences is evolving rapidly. Boarding schools that specialise in supporting learners with conditions such as dyslexia, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), executive-functioning issues, and other neurodiverse profiles are expanding their offerings and refining their approach. For families exploring this option, understanding how these boarding schools support students with learning differences can be crucial to making an informed decision.
In this article, we’ll explore how boarding schools address learning differences, highlight key support strategies, examine what parents and students should look for, share recent updates and examples, and provide a comparison of support models. The target keyword “boarding schools support students with learning differences” will be used naturally throughout.
The Case for Boarding Schools Supporting Students with Learning Differences
Boarding schools support students with learning differences by offering an environment designed for sustained, immersive support. In traditional settings, learners with dyslexia, ADHD, or executive-function difficulties may struggle with inconsistent support, large class sizes, or limited access to specialist staff. By contrast, boarding schools geared toward learning differences provide:
A total campus environment where academic, residential, social and emotional support are integrated.
Small class sizes, often 6:1, 4:1, or even smaller, which enable personalised instruction and monitoring. For example, The Gow School in New York reports a 4:1 student-to-faculty ratio in its learning differences programme.The Gow School+1
Faculty and staff who are trained in learning differences, evidence-based instruction, and executive function coaching.
Residential life staff who are aware of the learning profiles of the students and can reinforce strategies throughout the day and evening.
A culture of self-advocacy and growth mindset, where students with learning differences are encouraged to understand their strengths and needs in a structured, supportive environment.
In fact, according to a directory of boarding schools, there are currently 163 boarding schools offering dedicated programmes for students with learning differences, serving over 60,000 students in the 2025-26 school year.
This growth reflects increasing recognition that boarding schools support students with learning differences not just academically, but holistically.
Key Support Structures in Effective Programs
Below are central components of how boarding schools support students with learning differences.
1. Individualised Learning Plans &>
Schools develop learning profiles for each student, identifying strengths, challenges, prior accommodations (e.g., IEPs or 504 plans), and goals.
Based on these profiles, students receive individualised learning plans (ILPs) that address reading, writing, executive function, organisation, processing speed, and more.
Ongoing assessment and progress monitoring help adjust instruction and support as needed.
2. Small-Group & One-on-One Instruction
Many schools offer micro-classes, sometimes 3–8 students or fewer, specifically for students with learning differences. For example, the Blue Ridge School’s “Learning Centre” emphasises classes of three students or less when needed.
One-on-one tutoring, reading specialists, and writing clinics are common.
Instruction often uses multi-sensory, structured approaches (especially for language-based learning differences).
3. Executive Function Coaching & Life Skills
Students receive coaching in time management, organisation, planning, self-advocacy, and other executive-function skills.
Boarding students live on campus, enabling reinforcement of these skills in daily routines, homework sessions, dorm life, and weekend activities.
For example, the Gow School offers executive-function coaching as part of its structured programme.The Gow School
4. Integrated Residential Life & Social-Emotional Support
Staff in dormitories, residence life, and campus life are trained to support learners with differences — not only academically but socially and emotionally.
The 24/7 nature of boarding life means opportunities for intentional growth, peer mentoring, structured downtime, and remediation in a predictable environment.
Schools emphasise self-advocacy, peer support, and building confidence through community and leadership opportunities.
5. College & Post-Secondary Transition Planning
Because many students at these schools are college-bound, support extends to college advising, understanding accommodations in higher education, and transition planning.
Schools often help students articulate their learning differences positively, and prepare for the next step academically and socially.
Example: How One School Implements These Practices
Consider the example of Eagle Hill School:
The Eagle Hill School (Hardwick, Massachusetts) is a boarding and day school for students with diverse learning profiles including ADHD and dyslexia.Eagle Hill School They employ a nine-term academic year, tailor courses per student and family, and treat the dormitory as a learning environment (not merely a place to sleep). Their dorm counsellors are certified life coaches, helping extend academic and life-skills support beyond classroom hours.
This illustrates the holistic approach: when boarding schools support students with learning differences, they align academic, residential and social experiences to the student’s learning profile and growth trajectory.
What Parents and Students Should Evaluate
When evaluating how boarding schools support students with learning differences, families should consider the following factors:
| Factor | Questions to Ask |
|---|---|
| Learning difference expertise | Do faculty and staff have credentials/training in dyslexia, ADHD, executive function? Is there a dedicated learning-differences centre? |
| Class size & support ratio | What is average class size? What is the ratio for specialized support? Are there micro-classes? |
| Individualised plan | Is there an Individualised Learning Plan (ILP)? How often is it reviewed and adjusted? |
| Instructional methods | Are multi-sensory, structured reading/writing programmes used? Are executive-function skills explicitly taught? |
| Residential life integration | How are academic strategies reinforced in dorms, weekends, social life? Are dorm staff trained in learning differences? |
| College/pre-post-secondary transition | What support exists for transition to college or vocational settings? How do they prepare students to self-advocate for accommodations? |
| Culture & peer environment | Is the community inclusive, growth-oriented, and supportive of students who learn differently? |
| Outcomes & accreditation | What are the graduation and college-acceptance rates? Is the programme accredited and recognised for learning-differences support? |
By assessing through these dimensions, families can gauge how thoroughly a boarding school supports students with learning differences.
Recent Trends & 2025 Updates
Schools are increasingly emphasising executive-function training, self-advocacy and neurodiversity awareness as part of supporting students with learning differences — shifting beyond remediation to empowerment.
The Association of LD Schools (ALDS), founded in 2023, brings together schools specialising in learning differences (dyslexia, dyscalculia, dysgraphia, executive dysfunction) to share best practices and resources.ldschools.org
Schools are leveraging technology and assistive tools (e.g., speech-to-text, audiobooks, organisational apps) to support students with learning differences in boarding environments.
With increased awareness of mental health, many boarding schools support not only academic interventions but also anxiety, depression and self-regulation which often accompany learning differences. For example, the Lake Tahoe Preparatory School reported working with students who had learning differences alongside anxiety and depression.laketahoeprep.org
How Boarding Schools Support Students with Learning Differences: Summary Table
Here’s a concise summary of how boarding schools support students with learning differences:
| Factor | Questions to Ask |
|---|---|
| Learning difference expertise | Do faculty and staff have credentials/training in dyslexia, ADHD, executive function? Is there a dedicated learning-differences centre? |
| Class size & support ratio | What is average class size? What is the ratio for specialized support? Are there micro-classes? |
| Individualised plan | Is there an Individualised Learning Plan (ILP)? How often is it reviewed and adjusted? |
| Instructional methods | Are multi-sensory, structured reading/writing programmes used? Are executive-function skills explicitly taught? |
| Residential life integration | How are academic strategies reinforced in dorms, weekends, social life? Are dorm staff trained in learning differences? |
| College/pre-post-secondary transition | What support exists for transition to college or vocational settings? How do they prepare students to self-advocate for accommodations? |
| Culture & peer environment | Is the community inclusive, growth-oriented, and supportive of students who learn differently? |
| Outcomes & accreditation | What are the graduation and college-acceptance rates? Is the programme accredited and recognised for learning-differences support? |
Final Thoughts
When boarding schools support students with learning differences effectively, they provide more than a place to live and study: they create a fully integrated environment where the student’s learning profile is central to every part of daily life. For parents and students exploring this path in 2025, it’s important to look for a school that aligns instruction, residential life, and transition planning around the learner’s strengths and challenges.
Choosing a boarding school where learning differences are not an afterthought but the foundation of the programme can make a tremendous difference in academic success, confidence, and long-term growth. By evaluating the support structures, instructional philosophy, residential life integration, and outcomes, families can find a boarding school where students with learning differences not only keep up—they thrive.